Financial reporting is an essential process for any successful business, no matter how big or small they may be. It ensures that organizations have reliable, comprehensive data and insights into a company’s financial health, performance, and overall stability. Ultimately, this helps guide decision-making at all levels of an organization, from owners and investors to employees budgeting for projects and resources.
For small business owners, especially new ones, financial reporting can feel like a daunting task. What financial data do you need? How do you keep track of all your expenses? What kind of reports do you need to maintain? Who do you share your reports with?
In this blog post, we’ll answer those questions, explore the significance of financial reporting, shed light on the most important types of financial reports, and provide tips about how financial management for small businesses can streamline the financial reporting process.
The Importance of Financial Reporting for Small Businesses
Financial reporting is important to the long-term success of any business, but there are a few specific reasons that make small business financial management and reporting critical.
-
Transparency and Record Keeping:
-
The ultimate goal of financial reporting is to maintain an accurate and complete record of your finances. While you may officially file financial reports monthly, quarterly, or yearly, financial reporting is an ongoing process, which means businesses need a system to track every aspect of spending, income, customer invoices, losses incurred, and much more.
According to a recent
Small Business Owner survey by U.S. Bank, 80% of small business owners say their top stressor is securing enough funding to run their business. With a comprehensive record of your financials, you can offer the data and transparency that any investors, creditors, and partners need to understand your business’s financial position and make the decision to provide funding.
-
Compliance:
-
Every business must follow various financial regulations and tax laws, and failure to do so can lead to penalties and legal issues—a headache small business owners can’t afford.
Businesses must adhere to financial reporting standards and regulations set by governing bodies. For example, businesses in the U.S. must follow the
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) when preparing financial statements, so the results, according to the
Financial Accounting Foundation, are:
- “Relevant, representationally faithful, and reflective of economics
- Comparable with other organizations or governments
- Verifiable and auditable by a third party
- Understood by lenders, investors, donors, taxpayers, and others.”
To maintain these standards, small business owners that have some wiggle room in their budget should consider hiring a professional accountant or tax advisor to ensure compliance and reduce the risk of errors.
-
Strategic Planning:
-
Whether you’re doing it all on your own, have staff on-hand, or advisors backing you, you’ll need organized, accurate financial information to plan your business’s next move.
Through financial reports, companies can assess their performance over time, set the stage for growth, and use that data to make strategic decisions regarding expenses, expansion, investment, and cost-cutting measures, and other areas of improvement.

3 Key Financial Reports for Small Businesses
Financial reporting refers to the process of collecting, analyzing, and presenting financial information to stakeholders, including investors, creditors, and internal management. It includes various financial statements, including a balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement —more on those later.
-
1. Balance Sheet
-
A balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial health at a specific point in time. The generally accepted accounting equation for a balance sheet is broken down to: Assets = liabilities + owners’ equity.
Assets, any resources a business owns, are typically divided into three categories—current, fixed or investment, and intangible assets. Liabilities on the other hand are the costs that a company owe and can be current or long-term. And finally, equity, which mainly applies to corporations, includes retained earnings, common stock, treasury stock, and the owner’s investment into the business.
Using that equation, you should find that total assets are equal to the total balance of liabilities and equity. If not, you may have made an accounting error along the way.
-
2. Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement)
-
The income statement is a financial report that summarizes a company’s revenues and expenses over a specific period, typically a quarter or a year. It is divided into three sections: revenue, expenses, and profit or loss.
Expenses are a significant part of this statement and are categorized into operating and non-operating expenses.
Operating Expenses: These include costs directly related to a company’s core operations, such as employee salaries, rent, utilities, and marketing expenses. They are crucial for assessing the profitability of a business’s core activities.
Non-Operating Expenses: These expenses are not directly tied to a company’s primary operations, such as interest on loans or income taxes. While they may not reflect operational efficiency, they impact the overall profitability and tax liabilities of a business.
-
3. Cash Flow Statement
-
The cash flow statement tracks the flow of cash in and out of your business finances over a specific period. It categorizes cash inflows and outflows into operating, investing, and financing activities, and aims to show if these activities are helping cash flow or hurting it.
Essential Practices for Better Financial Reporting
Before diving into reports, there are a few ways to get yourself ahead of the curve, so the reporting process is as streamlined, organized, and accurate as possible.
-
Keep Detailed Records:
-
Accurate financial reporting starts with keeping detailed records of all financial transactions. This includes sales, expenses, payroll, and any other financial activities related to your business. Organize your records in a systematic manner, either electronically or on paper, to ensure easy access when needed.
-
Choose the Right Accounting Software:
-
Selecting the right accounting software is the first step towards mastering financial reporting. Modern accounting software simplifies the process of recording financial transactions, generating reports, and staying compliant with tax regulations. Popular options for small business finances include QuickBooks, Xero, and FreshBooks.
-
Create a Chart of Accounts:
-
A chart of accounts is a structured list of all your company’s accounts, making it easier to categorize and track financial transactions. It typically includes categories such as assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses. Setting up a well-organized chart of accounts is crucial for accurate financial reporting.
-
Separate Personal and Business Finances:
-
One common mistake among small business owners is mixing personal and business finances. It’s essential to keep separate bank accounts and credit cards for your business to simplify financial reporting and maintain clarity.
-
Monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
-
It’s critical to keep a close eye on key performance indicators (KPIs) that are relevant to your business. KPIs may include metrics like gross profit margin, inventory turnover, and customer acquisition cost. Monitoring these indicators will help you make data-driven decisions.
Empower Yourself and Your Business with Financial Reporting Software
As a small business owner, you have a lot on your plate to get done even before adding financial reporting to your to-do list. In fact, 83% of small business owners say they’re stressed by their workload and not having enough time to get everything done.
Digital solutions like financial reporting software or a spend management platform can save you time and stress by doing the heavy lifting for you. The tools on the market help streamline expense tracking, organize financial data, reduce human errors, and ensure compliance with financial reporting standards.
U.S. Bank’s Spend Management Platform is a card-based solution that gives businesses the real-time financial reporting and analytics they need to track spending, control payments, and aid in financial planning decisions.
There are a few features that are especially helpful to business owners as they create their financial reports.
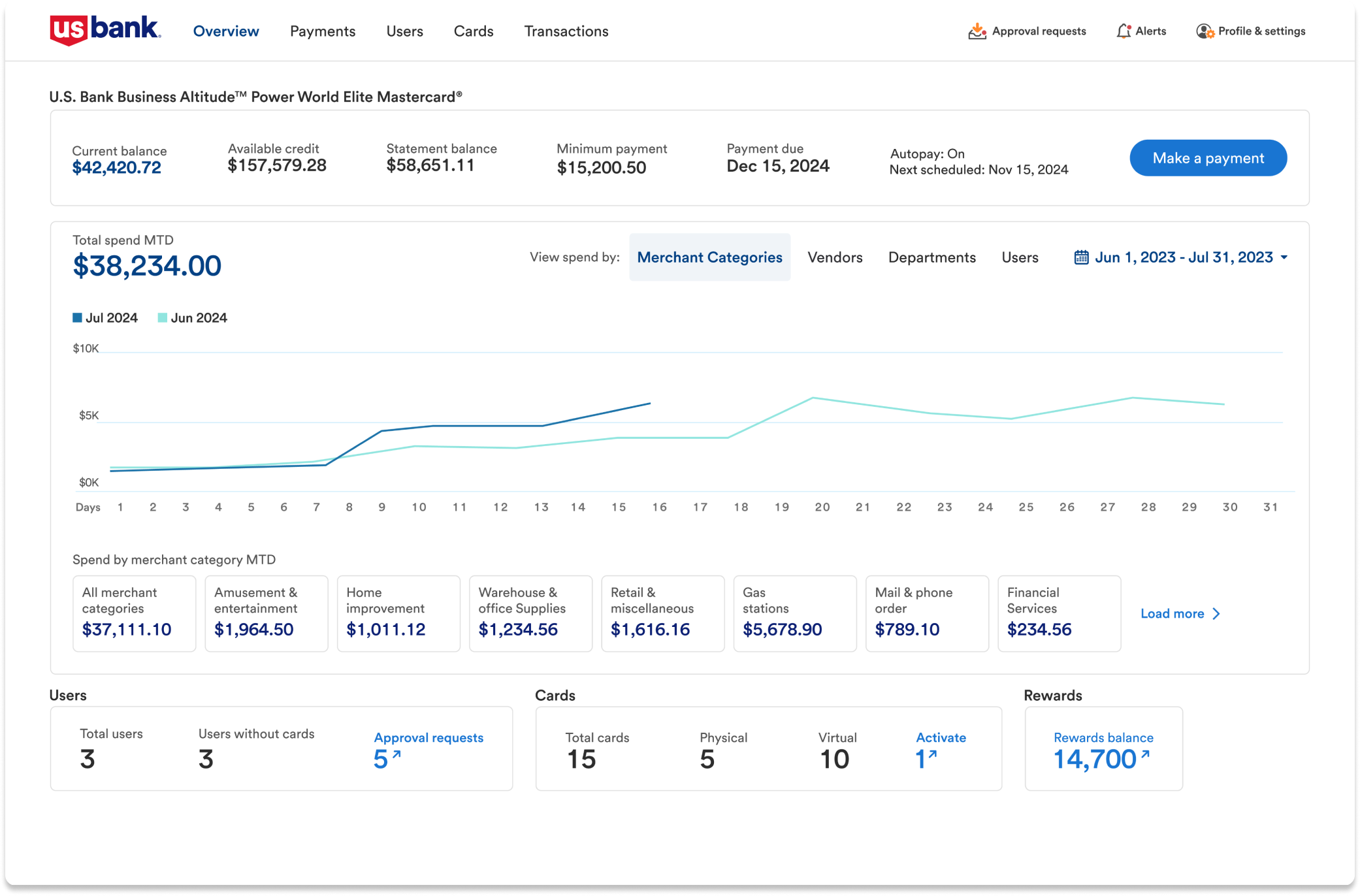
-
Total Spend Dashboard:
-
The Total Spend dashboard gives 360° view of your business finances with options to get down to the nitty gritty. For example, you can view spending by merchant categories, vendors, departments, or users i.e., your employees. Additionally, you’ll get a month-over-month comparison of spending which is a powerful way to identify spending patterns.
-
Transactions:
-
The Transactions tab of the Spend Management Platform has more incredibly useful data for financial reporting and offers two different views of your transactions: a simple Reporting view and an Accounting-focused view with enhanced functionality.
From there you can add filters to narrow in on specific transactions, review details of individual transactions, and even sync transactions with your accounting software for easier bookkeeping.
Both views can also be exported so you can easily save and/or share financial data.
-
Accounting Settings & Integrations:
-
U.S. Bank Spend Management also has
accounting settings and integration options that allow you to connect your preferred accounting software or configure your chart of accounts with customized GL account, class, and location values. These options keep your transactions organized and categorized, which help you streamline bookkeeping and
reconciliation.
The Bottom Line
Financial reporting is the bedrock of strategic, savvy decision-making for small businesses that leads to growth and resilience. With effective digital tools and financial reporting software, you’ll be better equipped to navigate the complexity of running a business and managing finances at the same time. Become the master of financial reporting, become the master of your business’s destiny.



